Timesaver summary
- CPU undervolting is an effective method for reducing PC heat, keeping your case cool, prolonging hardware life, and improving system stability. However, you need to take additional steps to properly adjust the CPU voltage and turn off the standard manufacturers settings, creating voltage spikes to extract additional performance.
- Undervolting is often associated with complex and risky settings typically used by tech enthusiasts. Traditional solutions and apps allow manual voltage adjustments, but they carry the risk of destabilizing your Windows system. Moreover, these solutions are not universally accessible—some apps only work on Intel, while others are exclusive to AMD.
- Camomile is a new app that makes undervolting easy, risk-free, and accessible. With just one button, it automatically reduces CPU voltage to a safe and recommended level, ensuring no risk to system stability. This app is free and works on both Intel and AMD chipsets. A link to download Camomile app.
Contents
- What is CPU undervolting, and why does each core react differently to voltage manipulations?
- Summary comparison table with an overview of of all possible solutions for undervolting a PC core.
- Detailed solution reviews: starting with the Camomile app review and ending with manual CPU tuning through BIOS.
- FAQ
What Is CPU Undervolting?
CPU undervolting is the process of reducing the voltage supplied to a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) without altering the clock speed or core frequency. The purpose of undervolting is to decrease the amount of power consumed by the CPU, which leads to lower temperatures, low heat, and, in some cases, improved efficiency.
When done correctly, undervolting does not compromise the performance of the CPU and can even enhance the overall stability and longevity of the hardware—this is what makes undervolting so attractive.
One input to consider
The creation of a CPU core is a highly complex and precise process that involves intricate design, cutting-edge fabrication techniques, and rigorous testing. From the initial concept to the finished product, it requires collaboration from many engineers, and each core has unique resources and characteristics.
Look at the graphs we have generated to illustrate changes in CPU core data over the last decade, including average time to market, R&D costs (in billions of US dollars), and core speed. The data highlights the increasing complexity, cost, and time associated with developing advanced CPU cores, while the rise in CPU clock speeds has been relatively slow.
Why does this even matter? Every core is a work of art
Core creation is a highly complex process—each core can have unique characteristics and react to voltage changes individually.
That is why we recommend adjusting the voltage gradually (if you are doing it manually) and monitoring the effects.
You can watch this short video to see all the stages of core creation.
(Spoiler: CPU manufacturing rooms are even cleaner than surgical rooms!)
No, undervolting cannot damage your PC
The worst outcome you might experience is that extremely low voltages could prevent your computer from booting. Extremely low voltage can also compromise your system’s stability, causing your PC to shut down during regular tasks and applications.
So, undervolting a CPU is generally safe if done correctly. CPUs vary in speed due to differences during manufacturing. Manufacturers test and label them based on their performance, including a safety margin. A CPU rated at 2.2 GHz might actually handle speeds up to 2.4 GHz under ideal conditions.
Lowering the voltage reduces a CPU’s speed. A 2.2 GHz CPU might drop to 2 GHz with undervolting. However, the only way to find a stable undervolt is to recuce voltage gradually and test system stability.
Testing stability means more than just booting the system. While it might boot fine at lower voltage, it needs to be tested under heavy loads and high temperatures (up to 85°C) to ensure it remains stable. Good tests include tasks like video compression or 3D rendering. If the PC remains stable, you’ve found a safe undervolt.
In our case study, we used an Excel spreadsheet with 1 million rows of random numbers and performed a search using the VLOOKUP formula—you can run similar tests as well.
Why do we need undervolting, and why are additional adjustments required?
Chipset manufacturers set default configurations often lead to peaks in power usage to maximize task performance, for instance, when you need a smooth picture during an intensive gaming session where numerous objects and particles are rendered on the screen simultaneously.
That’s when you see CPU temperature spikes up to 100°C, with the fans working at full speed.
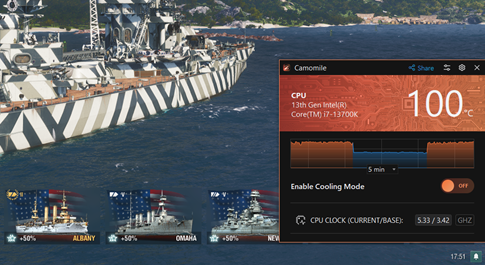
However, the nominal power of the chip is usually sufficient for everyday office and household use, keeping performance smooth and maintaining a comfortable temperature with minimal noise from the cooling system. This is often when people consider undervolting the CPU to keep their PC cooler.
However, there are no built-in system settings to adjust the core voltage, which is when we realize the need for additional apps and techniques.
Let’s review the various methods for undervolting. We’ll cover all available solutions and apps that allow you to undervolt the core, with a particular focus on the stability risks and accessibility.
Undervolting Solutions Overview
| Solution | General overview | Undervolting stability | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camomile Full review | Good solution The best “one-button” solution for safe and effective undervolting. Unprecedented accessibility for both AMD and Intel chipsets. Tech enthusiasts may find the lack of manual customization, advanced PC tweaks, and monitoring tools. | Good No room for manual, risky adjustments that can damage the system—safe undervolting activates automatically. All the changes are saved in a separate power plan profile that can be deleted to reverse the Camomile changes. | Good Works well with both Intel and AMD chipsets Supports Windows 10 and 11 |
| ThrottleStop Full review | Average solution Primarily suited for tech enthusiasts with Intel chipsets. | Low Allows manual voltage adjustments, which may pose a risk to system stability. | Low Supports Intel chipsets only; no AMD support. Compatible with Windows 7, XP, 10, and 11. |
| Intel XTU Full review | Average solution Primarily suited for tech enthusiasts with Intel chipsets, K- and X-series. | Low Allows manual voltage adjustments, which may pose a risk to system stability. | Low Supports Intel K- and X-series only;no AMD support. Windows 10,11 support. |
| Ryzen Master Full review | Average solution Primarily suited for tech enthusiasts with AMD chipsets. | Low Allows manual voltage adjustments, which may pose a risk to system stability. | Low Supports AMD Ryzen processors only; no Intel support. Windows 10,11 support. |
| ClockTuner for Ryzen Full review | Average solution The best solution for AMD Ryzen CPUs—minimizes stability risks by providing recommended voltage values for undervolting. | Good Calculates recommended undervolting figures, reducing the risk of system crashes. | Low Supports AMD Ryzen CPUs only; no Intel support. Compatible with Windows 10 and 11. |
| BIOS settings Full review | Average solution A challenging option for tech enthusiasts, as it relies on motherboard settings that often restrict undervolting options in the BIOS menu. | Low Allows manual voltage adjustments, which may pose a risk to system stability. | Low Many motherboards (both AMD and Intel) do not put undervolting settings in BIOS. |
How to Undervolt: All the Possible Apps and Solutions
Camomile App
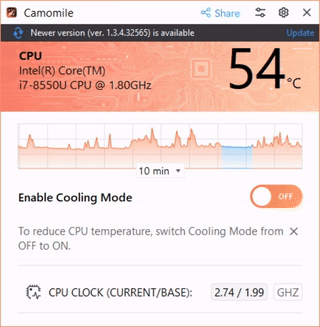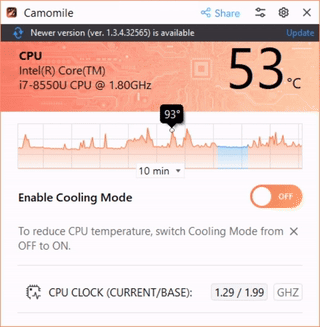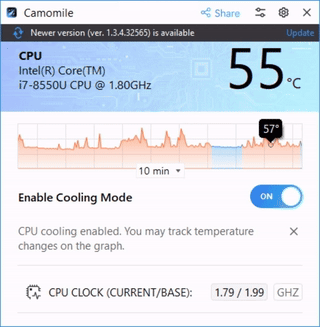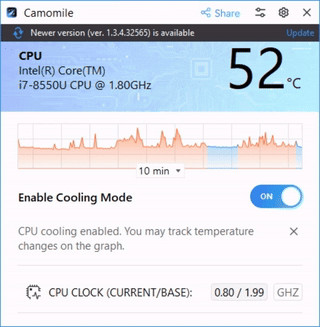
Camomile is a user-friendly application designed to simplify the process of CPU undervolting, making it accessible to both novices and experienced users. The app offers a one-click solution to automatically reduce CPU voltage to a recommended, safe level, ensuring minimal risk to system stability.
The app operates without complex manual configurations, streamlining the undervolting process. To undervolt your PC, you just need to install the app and turn on the button.
Features
- One-click undervolting: Camomile simplifies the undervolting process by offering a single-click solution that automatically adjusts CPU voltage to safe and recommended levels.
- Automatic safety adjustments: The app intelligently applies voltage settings that minimize risk to system stability, protecting the user from crashes and hardware issues.
- CPU temperature diagnostics: Camomile includes a built-in CPU temperature monitoring feature, allowing users to track the temperature of their processor in real-time, ensuring that undervolting is effectively reducing heat and maintaining safe operating conditions.
Pros
- Camomile eliminates the need for complicated manual settings, making it easy for users of all skill levels.
- The app is designed to apply safe, recommended voltage levels automatically, reducing the risk of system crashes or instability.
- Works on both Intel and AMD chipsets, providing flexibility across different systems.
- Camomile is completely free.
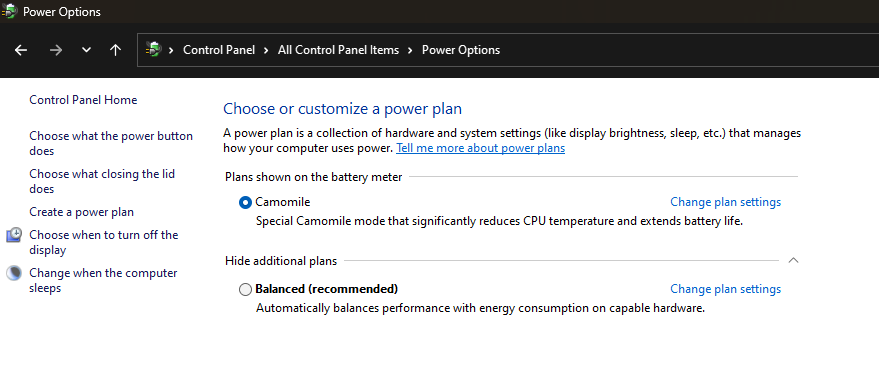
- Camomile creates a separate power plan profile that can be deleted to reverse all the changes.
Cons
- Advanced users may find the lack of manual control over voltage adjustments limiting.
- The app focuses solely on undervolting and doesn’t offer any additional performance optimization or monitoring tools.
Chipset support
Camomile supports both Intel and AMD chipsets, making it compatible with a wide range of processors.
OS support
Camomile is compatible with Windows 10,11. No Linux or Mac support.
ThrottleStop
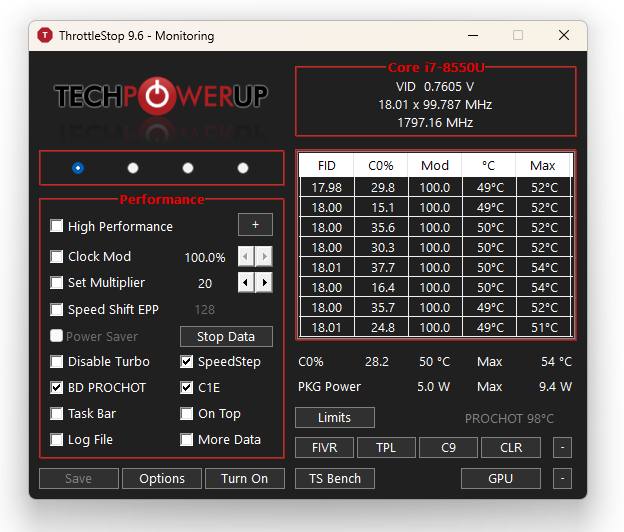
ThrottleStop is a performance monitoring and tweaking tool designed primarily for Intel-based CPUs. Its primary purpose is to control and bypass CPU throttling mechanisms like thermal, power, and voltage limits to ensure maximum performance.
It’s widely used to unlock the full potential of laptop CPUs, especially when they are artificially limited by the manufacturer to prevent overheating.
Undervolting in ThrottleStop
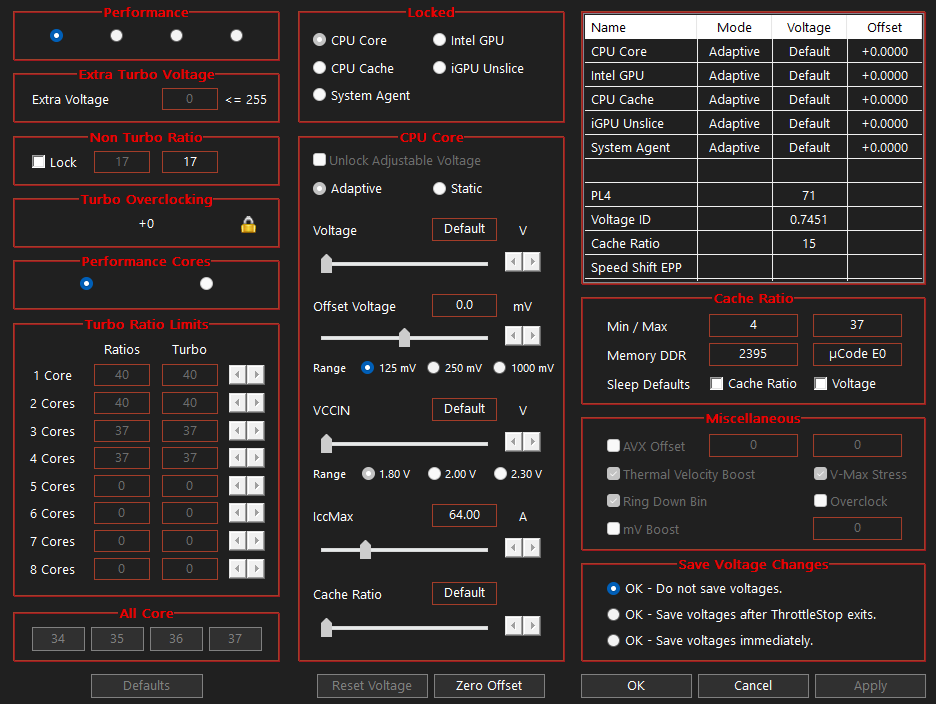
- Click on the FIVR button located in the main ThrottleStop window.
- Check the Unlock Adjustable Voltage box. This enables you to manually adjust the CPU voltage.
- Set OK – Save voltages immediately and click Apply. These settings let all changes in voltages come into effect immediately.
- Undervolt the CPU Core and CPU Cache under FIVR Control. Start by entering a small undervolt value, typically -50 mV for both CPU Core and CPU Cache.
Be aware that any changes to the core voltage can be risky and may affect system stability.
If you undervolt too aggressively, your PC may reboot, and the optimal settings would automatically recover. However, the software developer is not responsible for any potential damage to your system.
Features
- Undervolting: Allows users to reduce CPU voltage to lower temperatures and improve efficiency.
- Disable CPU throttling: Lets users bypass manufacturer-imposed limits like thermal throttling (TM1, TM2) and power limit throttling (PL1, PL2).
- Clock control: Adjusts the CPU’s core frequencies for both idle and high-performance modes.
- Profiles: Supports multiple performance profiles for different scenarios (e.g., gaming, battery saving, or heavy workloads).
- Real-time monitoring: Displays real-time statistics such as CPU temperature, clock speeds, and CPU load.
- BD PROCHOT override: Allows users to disable the “bi-directional processor hot” function, preventing the CPU from throttling based on signals from other components.
- Speed Shift (EPP): Fine-tunes Intel Speed Shift settings for faster response to dynamic CPU power adjustments.
- TS Bench: Built-in benchmarking tool to test CPU performance after adjustments.
Pros
- Provides users with detailed control over CPU performance, often not available through standard BIOS settings.
- The ability to create multiple performance profiles tailored for different use cases (gaming, general use, battery saving).
- ThrottleStop is a free tool, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
Cons
- Incorrect settings (e.g., too aggressive undervolting) can cause system instability, crashes, or freezes.
- The tool requires a good understanding of CPU behavior and throttling mechanisms; not beginner-friendly.
- It is community-supported and developed, meaning updates and bug fixes are not guaranteed or regular.
- AMD CPUs are not supported, restricting its use to Intel-based systems.
Chipset support
ThrottleStop is compatible with Intel CPUs, specifically focusing on mobile and desktop processors that support undervolting and various throttling mechanisms. It works particularly well with Intel Core i7, i5, and i3 chips, though support can vary based on the generation of the processor.
OS support
ThrottleStop is supported on Windows operating systems, particularly Windows 7, 8, 8.1, and 10. It has been reported to work on Windows 11, though this is not officially stated by the developer. It is not supported on macOS or Linux platforms.
Intel XTU (Extreme Tuning Utility)
Intel Extreme Tuning Utility is an advanced overclocking software designed by Intel. Its primary purpose is to provide users with an interface for fine-tuning their system’s performance, specifically focusing on Intel CPUs.
It allows users to overclock, undervolt, and adjust key system parameters, enhancing CPU performance, stability, and efficiency. XTU is primarily used by enthusiasts and power users who seek to maximize the performance of their Intel-based systems.
How to undervolt
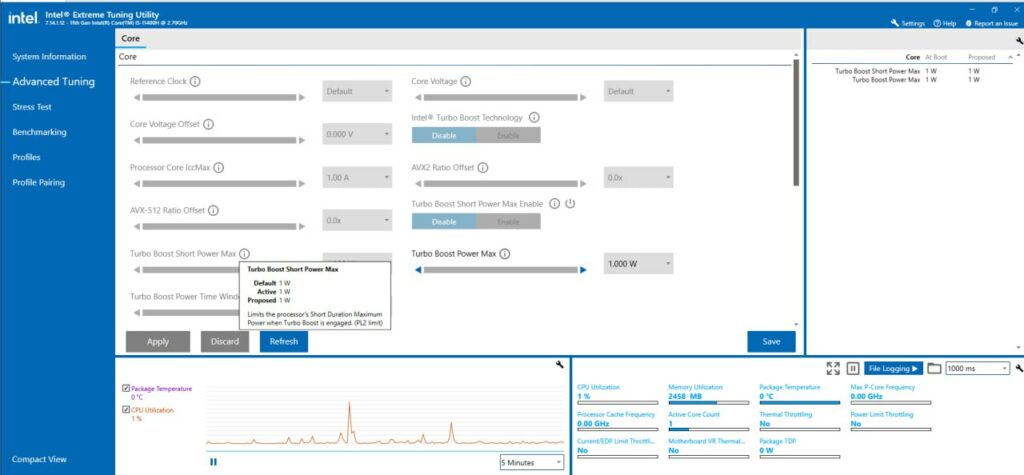
- Click on the Advanced Tuning tab on the left sidebar.
- This will open up detailed settings for the CPU, including voltage controls.
- In the Advanced Tuning section, locate the Core Voltage Offset option.
- Start with a small negative offset. Set a small negative value, such as -0.010V or -10 mV. Use either the slider or type in the value manually.
- After setting the Core Voltage Offset, click the Apply button.
After applying the undervolt, observe your system’s performance during regular use. Ensure that your system doesn’t crash or freeze.
To verify stability under load, go to the Stress Test tab. Run a stress test for 10-15 minutes to see how your system handles the new voltage. Watch for crashes or errors. If the system is unstable, you’ll need to reduce the undervolt.
Features
- Overclocking: Intel XTU provides controls for adjusting CPU clock speeds, voltage, and core ratios to overclock the processor for better performance.
- Undervolting: Allows users to reduce CPU voltage to lower power consumption and temperatures while maintaining performance.
- Memory tuning: Supports overclocking of RAM, allowing adjustments to frequency, voltage, and timings for optimized memory performance.
- Benchmarking tool: Includes a built-in benchmarking tool that allows users to test and compare the performance of their overclocking settings.
- Real-time monitoring: Displays real-time statistics of CPU temperatures, frequencies, power consumption, and system stability.
- Thermal throttling management: Lets users monitor and adjust settings to manage and minimize thermal throttling for better sustained performance.
- Profile management: Enables users to save and switch between different overclocking profiles for various performance or power-saving needs.
- Stress testing: Includes a stress-testing tool to evaluate the stability and thermal performance of the system after tuning adjustments.
Pros
- XTU offers an intuitive and well-organized interface, making it easier for users to access powerful overclocking and tuning features compared to BIOS.
- Includes a wide range of features such as overclocking, undervolting, memory tuning, stress testing, and benchmarking, making it a one-stop solution for performance tuning.
- Provides users with real-time data on critical system metrics, allowing for informed adjustments and safer overclocking.
- As an Intel-developed tool, it is optimized for Intel chipsets and processors, offering better compatibility and performance monitoring.
- Intel XTU is available for free, making it accessible to users who want to enhance their system’s performance without additional cost.
Cons
- Only works with Intel processors, excluding users with AMD CPUs from utilizing this tool.
- Certain changes may require a system reboot to apply, which can interrupt work or testing processes.
- Although user-friendly, some of the more advanced tuning options can be confusing or overwhelming for inexperienced users.
- Depending on the laptop model and cooling capabilities, XTU may be less effective or not fully functional for certain mobile processors.
Chipset support
Intel XTU is compatible with a limited range of Intel Core processors, including Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 models. It is specifically designed for Intel K- and X-series CPUs. Support varies by chipset and processor generation, so not all features are available for every Intel CPU. Older or low-power chipsets may have limited functionality. The whole list of supported chipsets is published on the official page (about ~100 chipsets).
We were very surprised that the list of the chipset is so wide and we get an official reply from Microsoft tech support – the list is definitely short.
OS support
Intel XTU is supported on Windows operating systems, particularly Windows 10 and 11. It does not officially support macOS or Linux, making it exclusive to Windows-based systems.
Ryzen Master
AMD Ryzen Master is a performance tuning utility designed for AMD Ryzen processors. The primary purpose of the software is to give users control over CPU overclocking, CPU undervolting, memory tuning, and system monitoring.
It caters to power users and enthusiasts who want to optimize their Ryzen-based systems for improved performance and higher clock speeds.
How to undervolt
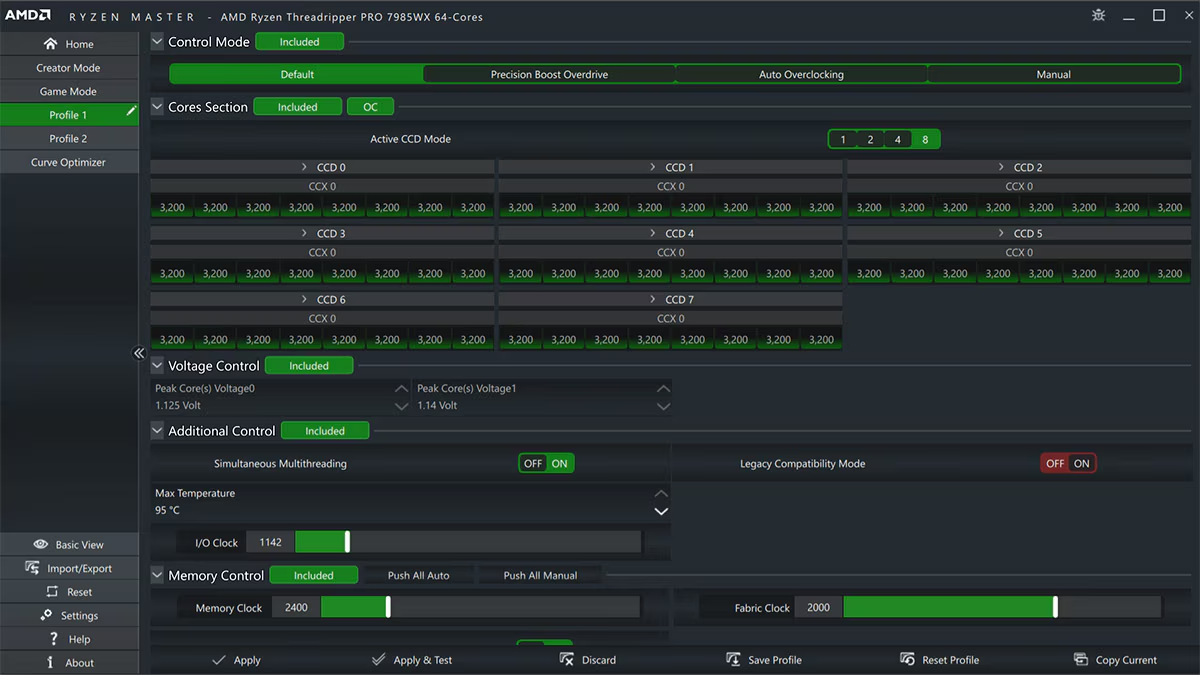
- Switch to Creator Mode (or Profile 1/Profile 2, depending on your preference). This mode provides advanced options for tuning voltage and clock speeds.
- Look for the voltage control setting, typically labeled as CPU Core Voltage (Vcore) or VDDCR CPU.
- Reduce the voltage by a small amount. For example, if the current voltage is 1.35V, reduce it to 1.30V. Or type in the new voltage value or use the sliders to adjust.
- Once you’ve adjusted the voltage, click Apply & Test in Ryzen Master. It will apply the changes and, in most cases, run a quick stability test.
If your system crashes or becomes unstable, increase the voltage slightly until stability is restored or reboot Windows to restore default settings.
Features
- CPU overclocking: Allows users to adjust core frequencies, voltage, and boost performance by overclocking individual cores or the entire CPU.
- Memory overclocking: Supports RAM tuning, including adjusting memory frequency, timings, and voltages to optimize memory performance.
- CPU undervolting: Supports CPU undervolting, enabling users to reduce power consumption and heat generation while maintaining performance.
- Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO): Lets users extend the CPU’s automatic boost capabilities by increasing power and thermal limits for higher performance.
- Profiles: Users can save custom overclocking and performance settings in multiple profiles for easy switching between different usage scenarios (e.g., gaming, productivity, power-saving).
- Per-core overclocking: Offers per-core control, allowing users to adjust each CPU core’s frequency and voltage individually for more granular tuning.
- Automatic overclocking: Provides an automatic tuning feature that adjusts settings for optimal performance with minimal user input.
- Real-time monitoring: Displays real-time information such as CPU temperatures, clock speeds, power usage, and CPU load, helping users monitor system health and performance.
- Stress testing: Built-in stress testing feature to verify the stability of overclocked or adjusted settings.
Pros
- Ryzen Master features a clear and intuitive interface that makes overclocking and tuning accessible to both beginners and advanced users.
- Allows for adjustments and monitoring in real time, eliminating the need to reboot into BIOS for every change.
- Provides control over various parameters, including per-core tuning, voltage control, and thermal limits, allowing for fine-tuned performance optimizations.
- Users can create and switch between performance profiles depending on their needs, such as gaming, content creation, or power saving.
- The software includes detailed monitoring tools to track system performance and detect potential overheating or instability issues.
Cons
- As with any overclocking software, changes made in Ryzen Master can lead to system instability, crashes, or even hardware damage if not done carefully.
- Ryzen Master is exclusive to AMD Ryzen processors, making it inaccessible to Intel CPU users or older AMD processors.
- Although many adjustments can be made in real time, some changes (such as certain voltage settings) still require a system reboot to take effect.
- Ryzen Master is designed for desktop processors and does not support AMD Ryzen mobile processors in laptops, limiting its usage to desktop PC users.
- While the software excels in CPU tuning, it does not offer comprehensive GPU overclocking options, which may require separate software.
Chipset support
Ryzen Master is compatible with AMD Ryzen processors, including Ryzen 3, 5, 7, 9, and Threadripper series CPUs. It is optimized for newer Ryzen chips and supports most X300/B300 series motherboards and above. However, certain features may be limited depending on the specific processor model and motherboard capabilities.
OS support
Ryzen Master is supported on Windows operating systems, specifically Windows 10 and Windows 11. There is no official support for macOS or Linux, so it is limited to users running Windows on their AMD-based systems.
ClockTuner for Ryzen (CTR)
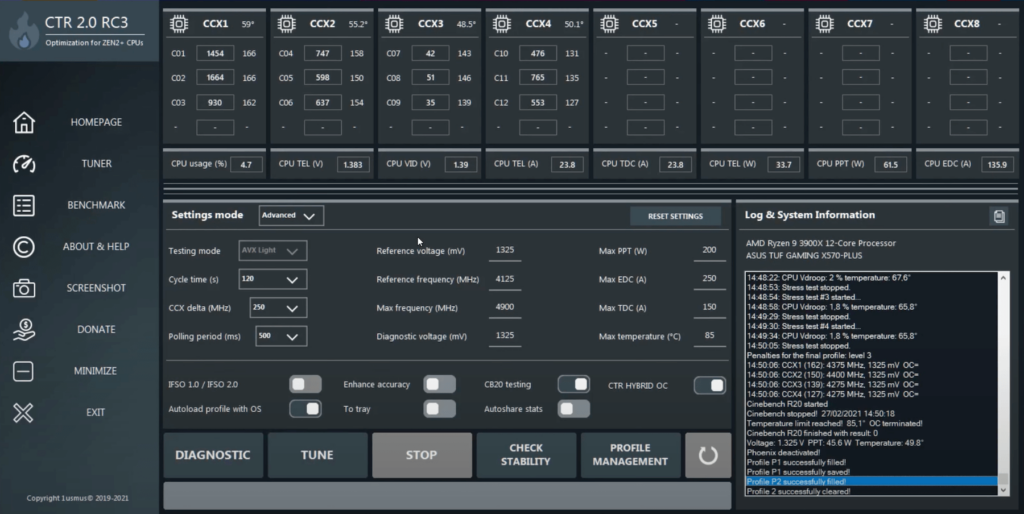
ClockTuner for Ryzen is a specialized tuning software designed specifically for AMD Ryzen processors. The purpose of CTR is to optimize the performance and efficiency of Ryzen CPUs by automatically adjusting the frequency and voltage of individual CPU cores based on their quality and workload.
CTR is aimed at enthusiasts and advanced users who want to maximize their CPU performance while maintaining power efficiency and lowering temperatures without the need for manual overclocking.
How to undervolt
Before making any adjustments, it’s important to run the diagnostic mode. This mode will test your CPU’s stock performance, temperature, and voltage to create a baseline profile.
Click the Diagnostic button and wait for the process to complete. CTR will assess your CPU’s capability and determine the optimal starting point for tuning. After the diagnostic test is complete, CTR will provide detailed results, including recommended undervolt settings and core performance data.
- FIT Voltage: This is the recommended safe operating voltage for your CPU.
- Temperature: Check your CPU’s temperature during the diagnostic process. Lower temperatures indicate room for further undervolting.
Now that you have the diagnostic results, it’s time to create an undervolting profile:
- Navigate to the Profile section in CTR (typically, Profile 1 or Profile 2).
- Adjust CPU core voltage. CTR will automatically suggest an undervolt value based on the diagnostic. For example, it might suggest reducing voltage by -0.050V or similar.
- Apply the suggested voltage values, but if you want to further lower the voltage, reduce it incrementally (e.g., reduce the voltage by another -0.010V at a time).
- After adjusting the voltage, click Apply Profile to implement the undervolted settings.
After setting the undervolt, continue to use your system normally and monitor its behavior under various workloads.
Features
- Automatic CPU undervolting: CTR performs automated core tuning by analyzing each CPU core’s performance and quality, then adjusts the voltage and frequency for optimal performance. This allows the software to extract higher performance without the risks associated with manual overclocking.
- Profile creation: CTR can generate multiple performance profiles for different workloads. Users can switch between profiles based on whether they need maximum performance (e.g., gaming or rendering) or efficiency (e.g., general use or light tasks).
- Per-core optimization: The software can analyze individual cores to detect high-performance and weaker cores, applying different settings to optimize the CPU’s overall stability and efficiency.
- Stress testing: CTR includes a built-in stress testing feature to ensure stability after tuning. It runs a series of stress tests to ensure the system remains stable under heavy loads, making it a reliable tool for overclocking enthusiasts.
- Adaptive frequency and voltage adjustment: CTR continuously monitors system performance and adjusts voltage and frequency dynamically based on load, helping maintain balance between power efficiency and performance.
- Temperature and power monitoring: CTR provides real-time monitoring of the CPU’s power consumption and temperature. It helps users see how their tuning efforts affect power efficiency and thermal performance.
- Easy-to-use interface: Despite its advanced functionality, CTR features a relatively simple and user-friendly interface. It provides detailed information but presents it in a way that is accessible for users familiar with CPU overclocking.
Pros
- The automated optimization process takes the guesswork out of manual overclocking, allowing users to achieve better performance and efficiency without deep technical knowledge.
- CTR’s ability to tune individual cores based on their quality ensures more stable and optimized performance compared to traditional all-core overclocking methods.
- By intelligently adjusting voltages, CTR can reduce power consumption and temperatures while improving performance, making it a great tool for users looking to enhance their CPU efficiency.
- The built-in stability tests and adaptive controls help reduce the risks of crashes or hardware damage, providing a safer environment for pushing the CPU beyond stock settings.
- CTR is completely free, providing a cost-effective solution for users wanting to improve the performance of their Ryzen processors.
Cons
- As its name suggests, ClockTuner for Ryzen is only compatible with AMD Ryzen CPUs, which means Intel users or those with older AMD processors cannot benefit from this software.
- While CTR automates much of the tuning process, the software still requires a solid understanding of CPU performance and system stability. Users unfamiliar with overclocking may find some of the concepts and terminology difficult to grasp.
- Occasionally, CTR may struggle with newly released Ryzen CPUs, especially during the early stages of compatibility updates, causing potential stability problems until updates are available.
- While CTR is designed to minimize risks, users may still encounter occasional system instability during tuning or heavy workloads, depending on the quality of their CPU’s cores.
Chipset support
ClockTuner for Ryzen supports a wide range of AMD Ryzen CPUs. Specifically, it is compatible with:
- Ryzen 3000 Series (Zen 2)
- Ryzen 5000 Series (Zen 3)
Compatibility with specific Ryzen models within these generations may vary based on updates to the software, so users should check the latest release notes from CTR’s developer.
OS support
ClockTuner for Ryzen is designed to work with Windows-based operating systems. CTR is fully supported and optimized for Windows 10, which is the recommended operating system for the software. While not originally developed for Windows 11, most recent versions of CTR have added support for the latest OS from Microsoft, ensuring compatibility for users who have upgraded. CTR does not support Linux or macOS platforms.
Undervolting a CPU via the BIOS
We don’t recommend using the BIOS to undervolt the CPU, as it can substantially affect system performance and lead to crashes. In case you still want to go with it, here is a quick guide:
- Restart your computer and press the appropriate key during startup to enter the BIOS (commonly Delete, F2, or F10, depending on your motherboard).
- Once inside the BIOS, look for a section labeled something like Overclocking, Advanced CPU Settings, or Voltage Control. The exact name will vary based on your motherboard manufacturer.
- In the overclocking section, find settings related to CPU voltage. It may be labeled as Vcore, CPU Voltage, or Core Voltage.
- If the CPU voltage is set to Auto, switch it to Manual or Offset Mode. Offset Mode: Choose a negative offset value (e.g., -0.050V or -50mV) to reduce the voltage. Start with small steps like -0.025V to test stability.
- Manual Mode: Enter a lower voltage manually (e.g., instead of 1.2V, try 1.15V). Start small to ensure stability.
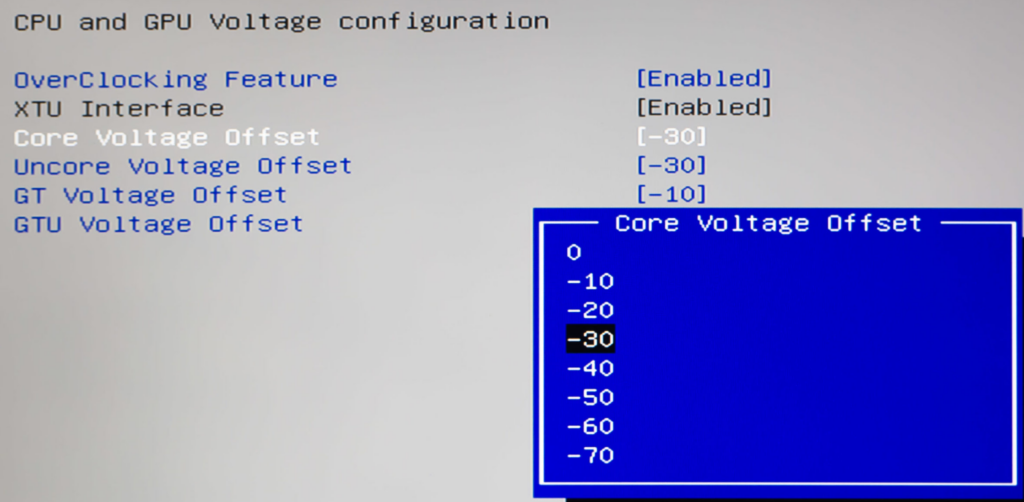
Once you’ve made the changes, save your settings (usually by pressing F10) and exit the BIOS. Your PC will reboot.
After rebooting, test the system stability using software like Prime95, AIDA64, or Intel Burn Test. Monitor your temperatures and performance to ensure the system is stable under load.
If your system crashes or becomes unstable, return to the BIOS and adjust the undervolt settings by reducing the amount (e.g., use a smaller offset).
FAQ
How Far Can we Undervolt CPU?
The extent to which you can undervolt a CPU depends on the specific model of the CPU and its individual characteristics. Generally, the process involves gradually lowering the voltage until you reach a point where the system becomes unstable or crashes. At this point, you increase the voltage slightly to ensure stability.
For most CPUs, you might be able to reduce the voltage by around 0.05V to 0.2V (50-200 mV), but this varies. Some CPUs may allow for a greater reduction, while others might only tolerate a small decrease before becoming unstable. The goal is to find the lowest stable voltage, where the CPU can still perform all its tasks reliably.
Can Undervolting Damage a PC?
It is safe and poses no risk of damaging your PC. In fact, it is considered safer than overvolting (increasing the voltage). By lowering the voltage, you reduce the heat and power consumption of the CPU, which can potentially extend its lifespan.
However, if the undervolt is too aggressive, it can cause instability in your system. This might result in random crashes, system freezes, or applications not working correctly. These issues can be resolved by adjusting the voltage slightly higher until the system becomes stable again. Unlike overvolting, which can generate excessive heat and potentially harm the hardware, undervolting does not risk overheating the CPU.